Gier Dunkle Instruments
DB-100 Infrared and MS-251 Solar Reflectometers
This technical review was kindly provided by University of Waterloo Professor Michael Collins:
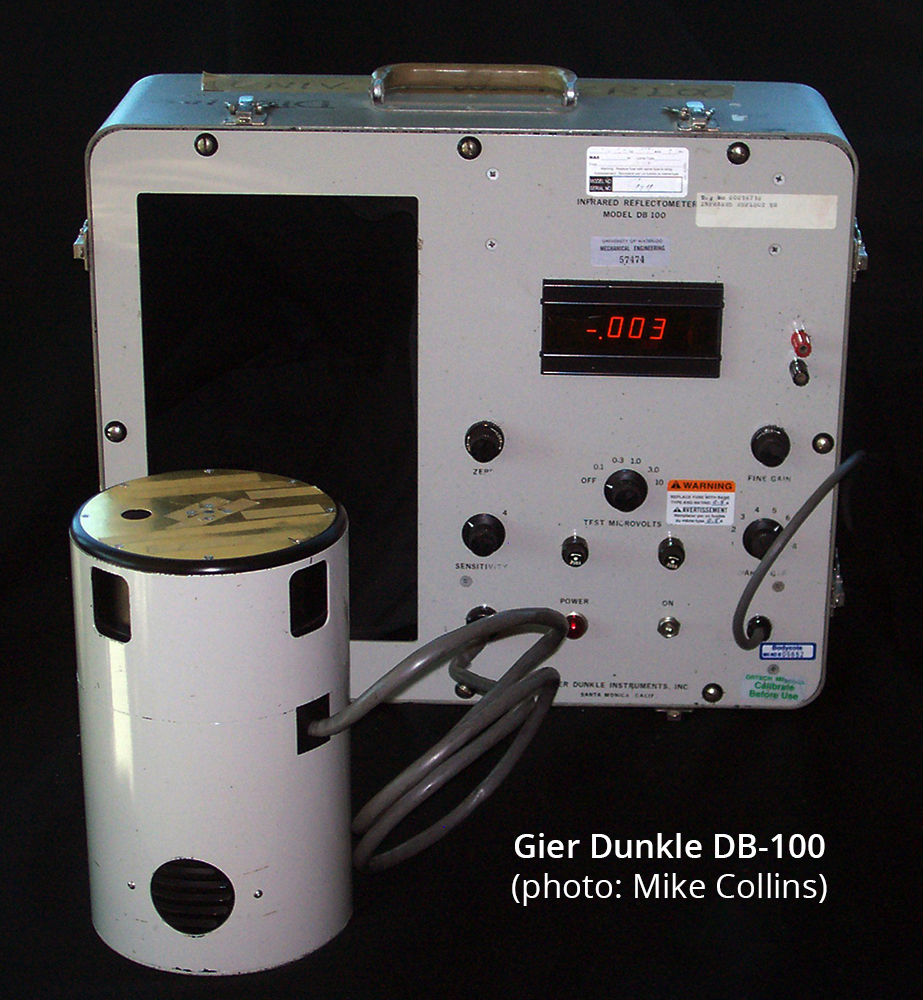 The DB-100 Infrared Reflectometer continues to be a very important piece of equipment. Up until 2013, it was the device that was needed to perform emissivity measurements according to ASTM E408, and I’m not entirely certain that any competing device even existed. In 2013, that standard was amended to include FTIR for measuring emissivity as Method C, although the process used by the Gier-Dunkle remains as Method A. I am regularly approached to do measurements using the DB-100 because (A) there are very few of these devices left in operation, and (B) it is fast, accurate, and still a valid ASTM measurement.
The DB-100 Infrared Reflectometer continues to be a very important piece of equipment. Up until 2013, it was the device that was needed to perform emissivity measurements according to ASTM E408, and I’m not entirely certain that any competing device even existed. In 2013, that standard was amended to include FTIR for measuring emissivity as Method C, although the process used by the Gier-Dunkle remains as Method A. I am regularly approached to do measurements using the DB-100 because (A) there are very few of these devices left in operation, and (B) it is fast, accurate, and still a valid ASTM measurement.
The DB-100 measures reflectance for room temperature thermal radiation. The sample, when placed over the sample port, is alternately exposed by the instrument to two different half-cylinders, one of which is maintained at ambient room temperature and the other heated slightly above room temperature. The sample is thereby alternately irradiated with radiation from a black body at room temperature and a black body slightly hotter than room temperature. The reflected plus emitted radiation from the sample is detected by a vacuum thermocouple, and converted to an AC signal. The AC component of the measured signal (representing part of only the reflected radiation) is then amplified and displayed. The instrument is calibrated just before use, using both a gold and a black standard of known IR reflectance. Once calibrated, the instrument is able to directly display the infrared reflectance of any sample. Due to the geometry of the instrument, the measured quantity is the hemispheric-normal IR reflectance of the sample.
If you were to pull out any undergraduate heat transfer text, and look at emissivity values in the appendix, those would have been obtained using a DB-100.* When industry was making the case to amend the ASTM standard to include FTIR, those devices were most often vetted by comparison to the Gier-Dunkle (e.g. Jaworske, D. and Skowronski, T. Portable Infrared Reflectometer for Evaluating Emittance, Presented at STAIF-2000, Albuquerque, NM, Jan 30-Feb 3, 2000)
 Years ago, the MS-251 Reflectometer would have been an cheap alternative to a UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer, but those spectrophotometers have become much cheaper, far more accurate, and able to provide spectral data (something the MS-251 can’t do). We haven’t used it for anything more than Graduate/Undergraduate lab equipment since 2002. To my knowledge, the impact of the MS-251 Solar Reflectometer was never close to the impact of the DB-100.
Years ago, the MS-251 Reflectometer would have been an cheap alternative to a UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer, but those spectrophotometers have become much cheaper, far more accurate, and able to provide spectral data (something the MS-251 can’t do). We haven’t used it for anything more than Graduate/Undergraduate lab equipment since 2002. To my knowledge, the impact of the MS-251 Solar Reflectometer was never close to the impact of the DB-100.
The MS-251 is a small scale integrating sphere. It’s operation is not that different from that of a spectrophotometer except that it has a single photosensor an no monochronometer.
Mike Collins, Ph.D., P.Eng.
Associate Chair Undergraduate Studies
Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering
University of Waterloo, Canada
February 18, 2019
*I’ve been told this on several occasions and believe it’s true. I can’t prove it though.
Directional Radiometer
From the chapter titled “Bioclimatic Factors and Their Measurement” (C.F. Kelly and T.E. Bond) in A Guide to Environmental Research on Animals:
Directional radiometers are designed to measure radiation intensity from a limited field of view, usually with the intent of measuring radiation from a particular source.
The Gier-Dunkle Directional Radiometer has as its sensing element a silver-constantan thermopile located at the bottom of a cone-shaped housing. The radiometer response is about 0.452 cal/cm2/min/mV. Fundamentally, such radiometers indicate the net heat transfer rate by radiation between the receiver element and the viewed object. If a black reference shield with known temperature is viewed, the net radiant transfer between it and the receiver will also be known. The thermopile irradiation can then be found by adding the black-body radiation of the shield to the difference between the two net radiant transfers (object and shield).
Bioclimatic Factors and Their Measurement
A Guide to Environmental Research on Animals
Page 55
Committee on Physiological Effects of Environmental Factors on Animals
Agricultural Board
National Research Council
National Academy of Sciences
Washington, D. C.
January 1, 1971